Hernia
[1] This may include pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, especially with coughing, exercise, or urinating or defecating.
[3] Groin hernias that do not cause symptoms in males do not need immediate surgical repair, a practice referred to as "watchful waiting".
[1] However most men tend to eventually undergo groin hernia surgery due to the development of pain.
[1] For women, however, repair is generally recommended due to the higher rate of femoral hernias, which have more complications.
[1] A hiatus hernia may be treated with lifestyle changes such as raising the head of the bed, weight loss and adjusting eating habits.
[1] Inguinal, femoral and abdominal hernias were present in 18.5 million people and resulted in 59,800 deaths in 2015.
[12] Most hernias happen when the muscles and tendons in the belly weaken or get damaged, which makes it hard for them to keep the insides in place and support the body properly.
[15] Healthcare costs associated with abdominal wall hernias account for an annual expenditure of approximately 2.5 to 3 billion dollars.
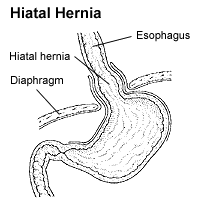
A hiatus hernia occurs when the stomach protrudes into the mediastinum through the esophageal opening in the diaphragm.
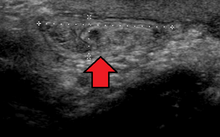
Hernias are caused by a disruption or opening in the fascia, or fibrous tissue, which forms the abdominal wall.
They may be chronic, although painless, and can lead to strangulation (loss of blood supply), obstruction (kinking of intestine), or both.
[22] Furthermore, conditions that increase the pressure of the abdominal cavity may also cause hernias or worsen the existing ones.
Some examples would be: obesity, straining during a bowel movement or urination (constipation, enlarged prostate), chronic lung disease, and also, fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites).
[23] Also, if muscles are weakened due to poor nutrition, smoking, and overexertion, hernias are more likely to occur.
If this type of hernia is due to blunt trauma it is an emergency condition and could be associated with various solid organs and hollow viscus injuries.
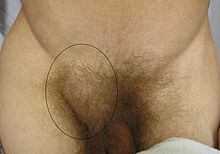
They involve protrusion of intra-abdominal contents through a weakness at the site of passage of the umbilical cord through the abdominal wall.
Umbilical hernias in adults are largely acquired, and are more frequent in obese or pregnant women.
An incisional hernia occurs when the defect is the result of an incompletely healed surgical wound.
[27] Higher in the abdomen, an (internal) "diaphragmatic hernia" results when part of the stomach or intestine protrudes into the chest cavity through a defect in the diaphragm.
A congenital diaphragmatic hernia is a distinct problem, occurring in up to 1 in 2000 births, and requiring pediatric surgery.
The above article deals mostly with "visceral hernias", where the herniating tissue arises within the abdominal cavity.
Using local anesthesia for open groin hernia repair, particularly in patients with additional health issues, leads to fewer complications and reduced costs.
[36] However, it might not be enough for repairing large hernias or in patients with abdominal domain loss, where general anesthesia is preferred.
The rates of overall complications, long-lasting postoperative pain, urinary retention, and 30-day re-admission are very similar between these two methods.
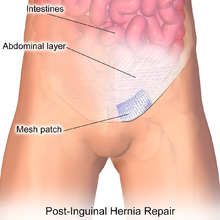
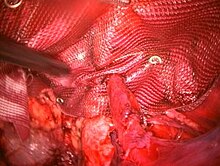
Muscle reinforcement techniques often involve synthetic materials (a mesh prosthesis[broken anchor]).
However, this widely used terminology is misleading, as there are many tension-free suture methods[broken anchor] that do not use mesh (e.g., Desarda, Guarnieri, Lipton-Estrin, etc.).
However, the use of prosthetic mesh appears to have a higher likelihood of causing long-term pain and can also lead to infections.
[43] Older age, femoral hernias, female sex, and urgent repair are identified as other factors linked to a higher risk of mortality.
To prevent a seroma it's important to reduce the amount of cutting around the hernia sac where it's connected to the cord structures.
Many patients are managed through day surgery centers and are able to return to work within a week or two, though intense activities are prohibited for a longer period.