M4 carbine
[10] Since its adoption in 1994,[9] the M4 has undergone over 90 modifications to improve the weapon's adaptability, ergonomics and modularity, including: the M4A1, which strengthened the barrel and replaced the burst-fire option with a fully automatic option; the SOPMOD, an accessory kit containing optical attachments; and the underbarrel weapons such as M203 and M320 grenade launchers to the Masterkey and M26-MASS shotguns.
In April 2022, the U.S. Army selected the XM7 rifle, a variant of SIG MCX Spear, as the winner of the Next Generation Squad Weapon Program to replace the M16/M4.
[21] The M4 carbine also replaced most submachine guns and selected handguns in U.S. military service,[21] as it fires more effective rifle ammunition that offers superior stopping power and is better able to penetrate modern body armor.
[24] While ordinary riflemen in the Marine Corps were armed with M16A4s, M4s were fielded by troops in positions where a full-length rifle would be too bulky, including vehicle operators, fireteam and squad leaders.
[27] In October 2015, Commandant Robert Neller formally approved of making the M4 carbine the primary weapon for all infantry battalions, security forces, and supporting schools in the USMC.
Upgrades included the heavier SOCOM barrel to better dissipate heat from sustained automatic firing, the full-auto trigger group with a more consistent trigger pull than the burst group's to enable better semi-automatic accuracy, and the ambidextrous selector lever for easier use with left-handed shooters.
[39][40] In addition to upgrade kits, in April 2012, the U.S. Army announced it would begin purchasing over 120,000 M4A1 carbines to start reequipping front line units from the original M4 to the new M4A1 version.
[47] The Heckler & Koch HK416 was introduced in 2005, incorporating the same lower receiver as the M4A1, but replacing its direct impingement system with a gas-operated rotating bolt, more comparable to that of the G36.
The ALP allows the operating rod to wiggle to correct for the downward pressure on the bolt and transfers the force straight backwards in line with the bore and buffer assembly, eliminating the carrier tilt.
The program aimed to replace the M4 Carbine and the M249 SAW with weapons that would compensate for their perceived deficiencies when fighting at longer ranges, as well as addressing concerns about the effectiveness of traditional 5.56x45mm ammunition against troops wearing body armor in a future peer or near-peer conflict.
SIG Sauer, Textron Systems, FN Herstal, True Velocity (previously Lonestar Future Weapons and General Dynamics), and PCP Tactical took part in the program.
The M4, and its variants, is a lightweight 5.56×45mm NATO (and .223 Remington) caliber, gas-operated, magazine-fed, air-cooled selective fire AR-15-pattern firearm.
The receiver is made of forged 7075-T6 aluminum, while the 14.5 in (368 mm) barrel, bolt, bolt carrier, and fire control group are made of steel; these components can be easily serviced and replaced by unit armories, enabling the addition of enhanced components and thus making the platform readily upgradable.
The furniture, including the buttstock, grip, and handguard are made of reinforced plastic, although the modular nature of the weapon means that these can be swapped by the end user.
Despite being its namesake, SOCOM itself has reverted to the original lighter "government profile" barrel while adopting a longer "mid length" gas system with its newer Upper Receiver Group-Improved (URG-I) modifications.
[34] The M4's maneuverability makes it beneficial for non-infantry troops (vehicle crews, clerks and staff officers), as well as for close quarters battle.
[58] Like all the variants of the M16, the M4 and the M4A1 can be fitted with many accessories, such as slings, night-vision devices, flash suppressors, suppressors, laser sights, telescopic sights, bipods, M9 bayonet, either M203 or M320 grenade launcher, M26-MASS shotgun, forward hand grips, a detachable rail-mounted carrying handle, or anything else compatible with a MIL-STD-1913 picatinny rail.
Exercises showed that having all weapons suppressed improved squad communication and surprise during engagements; disadvantages included additional heat and weight, increased maintenance, and the greater cost of equipping so many troops with the attachment.
18 CQBR may be issued as a standalone complete weapon system to SOCOM personnel, or as a separate upper receiver for their M4A1 to enable greater mission flexibility.
Although originally intended as an upper receiver kit for the M4A1 like the CQBR, the SPR would eventually be issued as a standalone complete rifle designated the Mk.
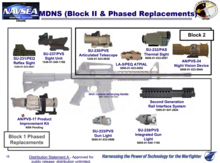
The SOPMOD Block II is a more radical modification kit for the baseline M4A1 that can be fitted at first-echelon unit maintenance level.
Other components of the Block II include the L3 Advanced Target Pointer Illuminator Aiming Laser (ATPIAL), or the AN/PEQ-15 as well as the LA5 high-power variants, and the ELCAN SpecterDR 1-4 optic.
The GAU-5/A Aircrew Self Defense Weapon (ASDW) is an Air Force modified M4 with a detachable barrel and handguard assembly, folding pistol grip, and fold-down iron sights to enable compact packaging.
This weapon is stowed in ejection seats of tactical aircraft and is intended to allow aircrew who egress in hostile environments to better defend themselves until rescue than existing handguns.
The Army said it planned to improve the M4 with a new cold-hammer-forged barrel to give longer life and more reliable magazines to reduce the stoppages.
The claimed benefits include less needed lubrication for the bolt carrier group to run reliably and reduced fouling.
Complicating the Army search for higher reliability in the M4 is a number of observations of M4 gas piston alternatives that suffer unintended design problems.
The third is that the use of a sound suppressor results in hot gases entering the chamber, regardless of a direct-gas impingement or gas piston design choice.
[95] In 2014, American firearms designer Jim Sullivan provided a video interview regarding his contributions to the M16 and M4 family of rifles while working for Armalite.
However, on December 8, 2005, a district court judge in Maine granted a summary judgment in favor of Bushmaster Firearms, dismissing all of Colt's claims except for false advertising.