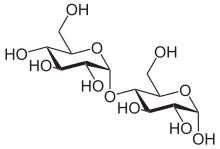
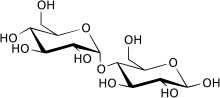
Maltose
Maltose (/ˈmɔːltoʊs/[2] or /ˈmɔːltoʊz/[3]), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond.
Maltose is the two-unit member of the amylose homologous series, the key structural motif of starch.
[5] Maltose was discovered by Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut, although this discovery was not widely accepted until it was confirmed in 1872 by Irish chemist and brewer Cornelius O'Sullivan.
[4] Carbohydrates are generally divided into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides depending on the number of sugar subunits.
The link is characterized as α because the glycosidic bond to the anomeric carbon (C1) is in the opposite plane from the CH2OH substituent in the same ring (C6 of the first glucose).