Mantoux test
The Mantoux test is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
It was also used in the USSR and is now prevalent in most of the post-Soviet states, although Soviet mantoux produced many false positives due to children's allergic reaction.
Purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin is a precipitate of species-nonspecific molecules obtained from filtrates of sterilized, concentrated cultures.
[2] It is named after Charles Mantoux, a French physician who built on the work of Koch and Clemens von Pirquet to create his test in 1907.
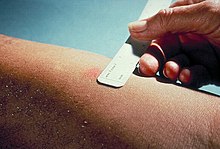
[6][7] In the Mantoux test, a standard dose of 5 tuberculin units (TU – 0.1 ml), according to the CDC,[8] or 2 TU of Statens Serum Institute (SSI) tuberculin RT23 in 0.1 ml solution, according to the National Health Service,[9] is injected intradermally (between the layers of dermis) on the flexor surface of the left forearm, mid-way between elbow and wrist.
A person who has been exposed to the bacteria would be expected to mount an immune response in the area of skin containing the bacterial proteins.
The reaction is read by measuring the diameter of induration (palpable raised, hardened area) across the forearm (perpendicular to the long axis) in millimeters.
High-risk groups include recent contacts, those with HIV, those with chest radiograph with fibrotic changes, organ transplant recipients, and those with immunosuppression.
[15] The Ohio Department of Health states that it give 80% of children protection against tuberculous meningitis and miliary tuberculosis.
[19] Reaction to the PPD or tuberculin test is suppressed by the following conditions: This is because the immune system needs to be functional to mount a response to the protein derivative injected under the skin.
A false negative result may occur in a person who has been recently infected with TB, but whose immune system hasn't yet reacted to the bacteria.
[citation needed] According to the US guidelines, latent tuberculosis infection diagnosis and treatment is considered for any BCG-vaccinated person whose skin test is 10 mm or greater, if any of these circumstances are present:[citation needed] In cases of anergy, a lack of reaction by the body's defence mechanisms when it comes into contact with foreign substances, the tuberculin reaction will occur weakly, thus compromising the value of Mantoux testing.
[citation needed] A person who is diagnosed as "infected in the distant past" on two-step testing is called a "tuberculin reactor".
[citation needed] According to the guidelines published by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2005, the results are re-categorized into 3 parts based on their previous or baseline outcomes:[citation needed] In addition to tuberculin skin tests such as (principally) the Mantoux test, interferon gamma release assays (IGRAs) have become common in clinical use in the 2010s.
The interferon gamma release assay is the preferred method for patients who have had immunosuppression and are about to start biological therapies.