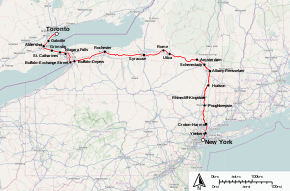
Maple Leaf (train)
The new Maple Leaf was the first collaboration between the two companies and the first direct New York–Toronto passenger service in a decade, the last being an overnight TH&B, New York Central, and Canadian Pacific Railway train called The Ontarian (Buffalo–Toronto) that ended in 1967.
While most Amtrak routes outside the Northeast Corridor had switched to the GE Genesis by 2000, it had not been added to the Maple Leaf owing to the Via Rail crews' unfamiliarity with the unit.
[8]: 107 The Maple Leaf is one of four New York Amtrak routes that are primarily state-funded with the others being the Adirondack, Empire Service, and Ethan Allen Express.
In 2013, the Maple Leaf was the target of a failed terror plot involving an attempt by two men, both permanent residents of Canada, who sought to derail the train as it crossed a bridge over the Twenty Mile Creek near Jordan, Ontario.
[9][10][11] In March 2020, the Maple Leaf was truncated to Niagara Falls, New York after all non-essential travel across the Canada–United States border was banned in response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
[14] The Adirondack and Maple Leaf was combined between New York and Albany–Rensselaer beginning November 10, 2024, due to construction work in the East River Tunnels limiting capacity at Penn Station.
All classes of service include complimentary WiFi, an electric outlet (120 V, 60 Hz AC) at each seat, reading lamps, fold-out tray tables.
Prior to the completion of the Empire Connection in 1991, the Maple Leaf originated at Grand Central Terminal in New York instead of Penn Station.
Southbound trains leave Toronto during the morning rush, cross into the United States just after noon and arrive in New York in mid-evening.