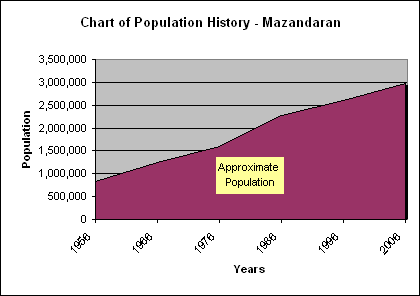
Mazandaran province
[13] Mazandaran is a major producer of farmed fish,[14] and aquaculture provides an important economic addition to traditional dominance of agriculture.
[10] Literally "the gate or the valley of the giants" from مازن (mâzan) + در (dar) + ـان (ân), from Avesta (Avestan: 𐬨𐬀𐬰𐬀𐬌𐬥𐬌𐬌𐬀, romanized: mazainiia, lit. 'giant').
In the early 20th century, Reza Shah connected northern Elbourz to the southern slopes by constructing seven new roads and railways, the provinces of Mazandaran and Gilan became known as Shomal by all Iranians (meaning "the North" in Persian).
The Amard were a tribe living along the mountainous region bordering the Caspian Sea, including current day Amol.
In 662 CE, ten years after the death of Yazdegerd III, the last Sasanian emperor, a large Muslim army under the command of Hassan ibn Ali invaded Tabarestan.
[24] This dynasty ruled the area till 645 AD, when Gil Gilanshah (a descendant of the Sasanian king Jamasp and a grandson of Piruz) joined Mazandaran to Gilan.
[25] Initially, the Rus' appeared in Serkland in the 9th century traveling as merchants along the Volga trade route, selling furs, honey, and slaves.
The Rus' undertook the first large-scale expedition in 913; having arrived on 500 ships, they pillaged the westernmost parts of Gorgan as well as Mazandaran and Gilan, taking slaves and goods.The Bavandids, who claimed descent from Kawus, provided three dynasties.
Pietro della Valle (1586–1652), who visited a town near Firuzkuh in Mazandaran, noted that Mazandarani women never wore the veil and didn't hesitate to talk to foreigners.
Mazandaran was the site of local wars in those years, which led to the transfer of the capital from Sari to Tehran by Fath Ali Shah.
Before the reign of Nader Shah, the province was briefly occupied by the Russian army in the aftermath of the Russo-Persian War (1722–23) and returned to Persia in 1735.
[citation needed] In the 19th century, during the reign of Fath-Ali Shah Qajar, the verdant region of Mazandaran was paid due attention as a recreational area.
[31][32] The eastern Gīlakī dialect is spoken in the entire valley of the Čālūs river, though Kurdish tribes were established in the yeylāq of Kojūr and Kalārdašt in the Qajar period.
The Alborz Mountain Range surrounds the coastal strip and the plains abutting the Caspian Sea like a huge wall.
There is often snowfall in the Alborz regions, which run parallel to the Caspian Sea's southern coast, dividing the province into many isolated valleys.
It covers 63,300 square kilometres (24,400 sq mi) and encompasses the southern and eastern slopes of the Alborz Mountains as well as their summits.
The Alborz range is composed of a granite core overlain with sedimentary rock including limestones, shales, sandstones, and tuffs.
The German traveller Samuel Gottlieb Gmelin, who visited this country in 1771, says that in the space of eight miles, on the road from Resht to Amot, 250 of such streams are to be seen, many of them being so exceedingly broad and deep, that the passage across is sometimes impracticable for weeks together.
These conditions result in the climatic division of the province into three types:[52]Mazandaran has 9 electoral fields and a total of 12 seats in the Islamic Consultative Assembly.
The first mention is implicit, when Fereydun sets its capital in a city called Tamishe near Amol: بیاراست گیتی بسان بهشت.................... به جای گیا سرو گلبن بکشت از آمل گذر سوی تمیشه کرد .............. نشست اندر آن نامور بیشه کرد And when Manuchehr is returning to Fereydun's capital, Tamisheh in Mazandaran (known as Tabarestan), after his victory over Salm and Tur.
[54] In the second section, a region called Mazandaran is mentioned in the Kai Kavoos era; it is an area which is mostly inhabited by Div (demons).
The current province was simply considered a part of Tabaristan; the name Mazandaran is a later development, perhaps based upon local terminology.
In the Mazandarani language of Iran in the Mazanderani calendar, the year is divided into 12 thirty-day months and one pentad of days, often beginning on March 21.
The custom of tying rainbow-colored bands on wrists, which are worn for ten days and then thrown into a stream, is also a way to rejoice for children.
Other famous events like, Varf chal, traditional ceremony with almost 800 years old as one of the unique rituals of Mazandaran associated with water was held in the village of Ab Ask and Lochu Wrestling game in different time.
Music in this region relates to the lifestyle of the inhabitants, and the melodies revolve around issues such as the forests, cultivation or farming activities and herding.
More than 800 registered historical and cultural sites, 338 kilometers of shorelines, mineral springs in jungles and mountains, waterfalls, and caves are among the major tourism attractions in the Mazandaran province.
Rice, grain, fruits, cotton, tea, tobacco, sugarcane, Flower, Mineral water, caviar, Dairy product, Meat industry and silk are produced in the lowland strip along the Caspian shore.
[70][71][72] Germany, Russia, Iraq, France Turkey, Kazakhstan, India, Malaysia, United Arab Emirates, Afghanistan, Belarus, Italy, Bahrain, Pakistan, Switzerland Ukraine, United States, Spain, Netherlands and Central Asian countries were Mazandaran's main export destinations during the period.
Weightlifting, Taekwondo, table tennis, boxing, kickboxing, kung fu, karate, rally car are other successful sports in the province.