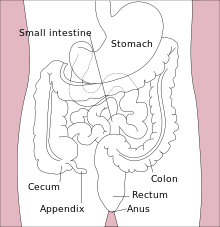
McBurney's point
McBurney's point is located one third of the distance from the right anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus (navel).
[1][2] This point roughly corresponds to the most common location of the base of the appendix, where it is attached to the cecum.
Specific localization of tenderness to McBurney's point indicates that inflammation is no longer limited to the lumen of the bowel (which localizes pain poorly), and is irritating the lining of the peritoneum at the place where the peritoneum comes into contact with the appendix.
Tenderness at McBurney's point suggests the evolution of acute appendicitis to a later stage, and thus, the increased likelihood of rupture.
[6] A pseudoaneurysm in the aorta may be treated surgically, with an incision made between McBurney's point and the lower intercostal spaces.