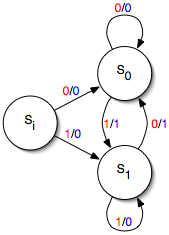
Mealy machine
This is in contrast to a Moore machine, whose output values are determined solely by its current state.
A Mealy machine is a deterministic finite-state transducer: for each state and input, at most one transition is possible.
"Evolution across time" is realized in this abstraction by having the state machine consult the time-changing input symbol at discrete "timer ticks"
This graph is a union of disjoint cycles if the automaton is bireversible[definition needed].
(In this example, the output is the exclusive-or of the two most-recent input values; thus, the machine implements an edge detector, outputting a 1 every time the input flips and a 0 otherwise.)
Considering the input and output alphabet the Latin alphabet, for example, then a Mealy machine can be designed that given a string of letters (a sequence of inputs) can process it into a ciphered string (a sequence of outputs).
Modern CPUs, computers, cell phones, digital clocks and basic electronic devices/machines have some kind of finite state machine to control it.
Simple software systems, particularly ones that can be represented using regular expressions, can be modeled as finite state machines.
There are many such simple systems, such as vending machines or basic electronics.
By finding the intersection of two finite state machines, one can design in a very simple manner concurrent systems that exchange messages for instance.