Measurement in economics
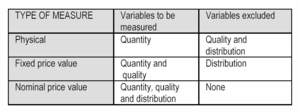
Quality as a variable refers to qualitative changes in the production process.
Qualitative changes take place when relative of different constant-price input and output factors alter.
Distribution as a variable of the production refers to a series of events in which the unit prices of constant-quality products and inputs alter causing a change in income distribution among those participating in the exchange.
If the presumed unchanged quality is not realized, the measurement gives results which are hard to interpret.
In this case, the results are affected by changes in both quantity and quality but in which proportion is unknown.
Return and costs in the loss and profit statement are typical examples of a nominal price.
In short-term reviews with only little production income distribution taking place, nominal price values are well suited for estimates of fixed price values.