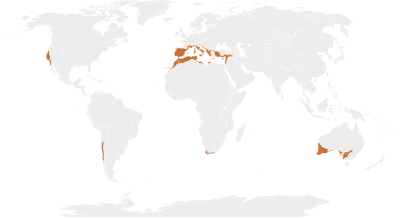
Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub
[citation needed] Phytogeographers consider the fynbos (South Africa) as a separate floral kingdom because 68% of the 8,600 vascular plant species crowded into its 90,000 square kilometers (35,000 sq mi) are endemic and highly distinctive at several taxonomic levels.
In both the Australian and Californian Mediterranean-climate eco-regions, native peoples used fire extensively to clear brush and trees, making way for the grasses and herbaceous vegetation that supported game animals and useful plants.
Today, frequent accidental ignitions can convert chaparral from a native shrubland to non-native annual grassland and drastically reduce species diversity, especially under drought brought about by climate change.
[6][7] On 25 July 2023, devastating wildfires were burning in at least nine countries across the Mediterranean, including Croatia, Italy, and Portugal, with thousands of firefighters in Europe and North Africa working to contain flames stoked by high temperatures, dry conditions, and strong winds.
Many have suffered tremendous degradation and habitat loss through logging, overgrazing, conversion to agriculture, urbanization, fire suppression, and introduction of exotic and invasive species.
The ecoregions around the Mediterranean basin and in California have been particularly affected by degradation due to human activity, suffering extensive loss of forests and soil erosion, and many native plants and animals have become extinct or endangered.