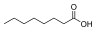
Medium-chain triglyceride
Medium-chain triglycerides are generally considered a good biologically inert source of energy that the human body finds reasonably easy to metabolize.
[15] However, there is other evidence demonstrating no risk of ketoacidosis or ketonemia with MCTs at levels associated with normal consumption,[8] and that the moderately elevated blood ketones can be an effective treatment for epilepsy.
[4] Due to their ability to be absorbed rapidly by the body, medium-chain triglycerides have found use in the treatment of a variety of malabsorption ailments.
[4][19][20] Orally ingested medium chain triglycerides would be very rapidly degraded by first-pass metabolism by being taken up in the liver via the portal vein, and are quickly metabolized via coenzyme A intermediates through β-oxidation and the citric acid cycle to produce carbon dioxide, acetate and ketone bodies.
[21][22][23][24] MCTs are bland compared to other fats and do not generate off-notes (dissonant tastes) as quickly as LCTs.
Because of these attributes, they are widely used as carrier oils or solvents for flavours and oral medicines and vitamins.