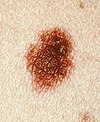
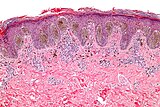
Melanocytic nevus
Common mole hair removal procedures include plucking, cosmetic waxing, electrolysis, threading, and cauterization.
When melanocytes are produced at an extremely rapid rate, they form in clusters instead of spreading out evenly, resulting in abnormal skin pigmentation in some areas of the body.
Researchers hypothesized that overexposure to UV, including excessive sunlight, may play a role in the formation of acquired moles.
Some strong indications supporting this hypothesis (but falling short of proof) include: Studies have found that sunburns and excessive sun exposure can increase risk factors for melanoma.
To prevent and reduce the risk of melanoma caused by UV radiation, the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Cancer Institute recommend: Clinical diagnosis can be made with the naked eye using the ABCD guideline or by using dermatoscopy.
Melanocytic nevi can mainly be classified by depth, being congenital versus acquired, and/or specific dermatoscopy or histopathology patterns: Specific dermatoscopy or histopathology patterns In this case, the central portion is a complex papule, and the periphery is macular, irregular, indistinct and slightly pink.
Other warning signs include a mole, even if smaller than a pencil eraser, that is different from the others and begins to crust over, bleed, itch, or become inflamed.
Lesions which greatly deviate from the common characteristics are labeled as an "ugly duckling", and further professional exam is required.
[citation needed] The "little red riding hood sign",[27] suggests that individuals with fair skin and light colored hair might have difficult-to-diagnose melanomas.
[citation needed] Extra care and caution should be rendered when examining such individuals as they might have multiple melanomas and severely dysplastic nevi.
A dermatoscope must be used to detect "ugly ducklings", as many melanomas in these individuals resemble non-melanomas or are considered to be "wolves in sheep clothing".
People with a personal or family history of skin cancer or of dysplastic nevus syndrome (multiple atypical moles) should see a dermatologist at least once a year to be sure they are not developing melanoma.
If the lesion is a seborrheic keratosis, then shave excision, electrodesiccation, or cryosurgery may be performed, usually leaving very little, if any scarring.
If a melanocytic nevus is suspected of being a melanoma, it needs to be sampled or removed via skin biopsy, and sent for microscopic evaluation by a pathologist.
Shaving leaves a red mark on the site but changes to the patient's usual skin color in about 2 weeks.
For surgery, many dermatologic and plastic surgeons first use a freezing solution, usually liquid nitrogen, on a raised mole and then shave it away with a scalpel.
Electric currents are set to a level such that they only reach the outermost layers of the skin, thus reducing the problem of scarring.
[citation needed] Third, similar to other surgeries, there is also risk of infection, allergic reactions to anesthesia, or even nerve damage.
Rather, most moles were considered hideous growths that appeared mostly on the noses, cheeks, and chins of witches, frogs, and other low creatures.
[citation needed] During the Salem witch trials, warts and other dermatological lesions such as moles, scars, and other blemishes, found on accused women were considered evidence of a pact with the devil.