Memory improvement
There are different techniques to improve memory, some of which include cognitive training, psychopharmacology, diet, stress management, and exercise.
After the learning of London taxicab drivers, who memorize maps of the city while studying to drive taxis, was studied over a period of time, it was found that the grey matter volume increased in the posterior hippocampus, an area in the brain involved heavily in memory.
The longer taxi drivers navigated the streets of London, the higher the volume of the gray matter in their posterior hippocampus.
This suggests a correlation between mental training or exercise and the brain's capacity to manage greater volume and more complex information.
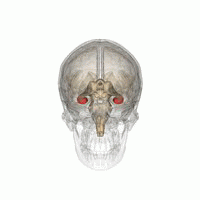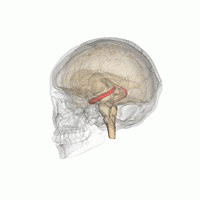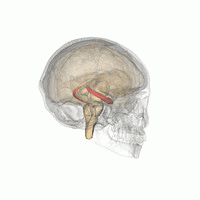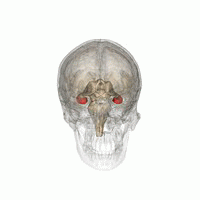
[2] Research has found that chronic and acute stress have adverse effects on memory processing systems.
Expectancy and effort effects occur when the experimenter subconsciously influences the participants to perform a desired result.
An example is to generalize findings of a single task and interpret the observed improvements as a broadly defined cognitive ability.
The system was created by Dr. Peter Marshall for research purposes at Royal Holloway, University of London.
[19] The testing effect happens when most of the learning is allocated to declarative knowledge and long term memory is enhanced.
Encountering previously learned information after a break helps improve long- and short-term retention.
[28] These diagrams are beneficial because they require the creator to link and integrate different ideas, which improve critical thinking and leads to more meaningful learning.
[21] Concept maps have been shown to improve people's ability to complete novel problem solving tasks.
[32] The method of loci is a technique utilized for memory recall when items to be remembered are associated with different locations that are well known to the learner.
[21] There are limitations when using method of loci, since it is difficult to recall any given item without working one's way through the list sequence, which can be time consuming.
[13] The changes are potentially long-lasting, as meditation may be able to strengthen neuronal circuits as selective attention improves.
Research shows that mindfulness can improve memory, which influences stress processing pathways in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex.
[43] In both human and animal studies, exercise has been shown to improve cognitive performance on encoding and retrieval tasks.
[45] Ongoing exercise interventions have been found to favorably impact memory processes in older adults[46] and children.
Hippocampus-dependent learning can promote the survival of newborn neurons, which may serve as a foundation for the formation of new memories.
[44] A meta-analysis concluded that resistance training, as compared to cardiovascular exercise, had no measurable effect on working memory.
[53] Similarly, adults with no previous musical training who participated in individualized piano instruction showed improved performance on tasks designed to test attention and working memory compared to a healthy control group.
[55] Another study tested how learning a new activity impacts the memory and mental control of elderly patients.
[56] Physical memory aids, which are typically worn on the wrist or finger, can help the user remember something they might otherwise forget.
It was originally invented by physicist Rick Yukon, who used visuals that were difficult to ignore with a deliberately intrusive shape and size.
[62] Other methods for remembering things include writing on one's own hand, sending a text message to oneself, or using sticky notes.