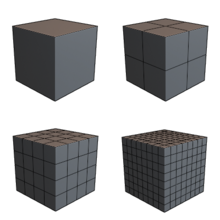
Subdivision surface
Less commonly, a simple algorithm is used to add geometry to a mesh by subdividing the faces into smaller ones without changing the overall shape or volume.
This process produces a denser mesh than the original one, containing more polygonal faces (often by a factor of 4).
Mathematically, the neighborhood of an extraordinary vertex (non-4-valent node for quad refined meshes) of a subdivision surface is a spline with a parametrically singular point.
[3] Subdivision surface refinement schemes can be broadly classified into two categories: interpolating and approximating.
In general, approximating schemes have greater smoothness, but the user has less overall control of the outcome.
[clarification needed] There are five approximating subdivision schemes: After subdivision, the control points of the original mesh and the newly generated control points are interpolated on the limit surface.