Metal–halogen exchange
The reaction commonly involves the use of electropositive metals (Li, Na, Mg) and organochlorides, bromides, and iodides.
Farnham and Calabrese crystallized an "ate-complex" lithium bis(pentafluorophenyl) iodinate complexed with TMEDA.
[7] A number of kinetic studies also support a nucleophilic pathway in which the carbanion on the lithium species attacks the halogen atom on the aryl halide.
In reactions of secondary and tertiary alkyllithium and alkyl halides, radical species were detected by EPR spectroscopy.
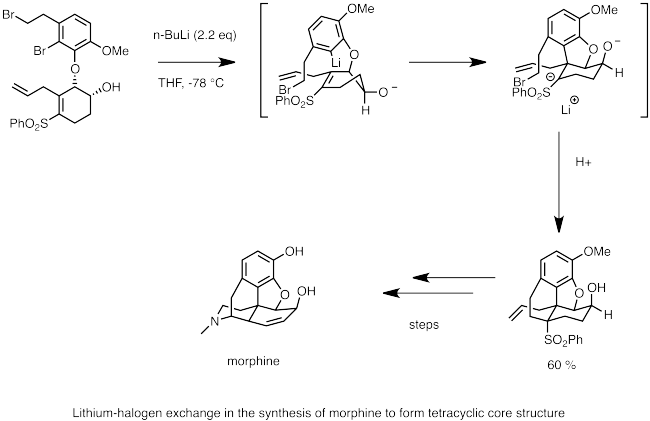
The nucleophilic carbanion center quickly undergoes carbolithiation to the double bond, generating an anion stabilized by the adjacent sulfone group.
[15] In this reaction, an aryl halide (usually iodide or bromide) exchanges with organolithium to form a lithiated arene species.
If the arene bears a side chain with an electrophillic moiety, the carbanion attached to the lithium will perform intramolecular nucleophilic attack and cyclize.