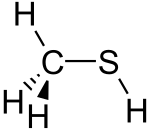
Methanethiol
It is a natural substance found in the blood, brain and feces of animals (including humans), as well as in plant tissues.
Due to alkalinity, MeSH is readily deprotonated (MeSNa), and the formed MeS− ion is also a strong nucleophile, reacting further to dimethyl sulfide.
The compounds remain in the liquor and are burned in the recovery boiler, where the sulfur is recovered as sodium sulfide.
[4] Methanethiol is released from decaying organic matter in marshes and is present in the natural gas of certain regions, in coal tar, and in some crude oils.
In surface seawater, methanethiol is the primary breakdown product of the algal metabolite dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP).
[11] Methanethiol is mainly used to produce the essential amino acid methionine, which is used as a dietary component in poultry and animal feed.
[12] The safety data sheet (SDS) lists methanethiol as a colorless, flammable gas with an extremely strong and repulsive smell.
[14] On November 15, 2014, at DuPont's La Porte, Texas facility, 24,000 pounds of methyl mercaptan was released and travelled downwind into surrounding areas, killing four and injuring one other.
Many believed they were experiencing a natural gas leak, which led to a high volume of emergency calls and the closure of several local government offices.