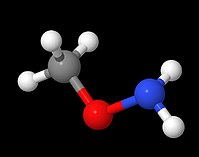
Methoxyamine
Also called O-methylhydroxylamine, it is a colourless volatile liquid that is soluble in polar organic solvent and in water.
Alternatively, it can be viewed as a derivative of methanol with the hydroxyl hydrogen replaced by an amino group.
For example, it is obtained by O-methylation of acetone oxime followed by hydrolysis of the O-methylated oxime:[4] The other broad method involves methanolysis of hydroxylamine sulfonates: Analogous to the behavior of hydroxylamine, methoxyamine condenses with ketones and aldehydes to give imines.
This N-lithio derivative is attacked by organolithium compounds to give, after hydrolysis, amines:[5] Methoxyamine has potential medicinal uses.
It covalently binds to apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) DNA damage sites and inhibits base excision repair (BER), which may result in an increase in DNA strand breaks and apoptosis.This agent may potentiate the anti-tumor activity of alkylating agents.