Methylrhenium trioxide
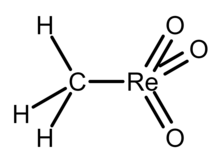
Methylrhenium trioxide, also known as methyltrioxorhenium(VII), is an organometallic compound with the formula CH3−ReO3.
In this compound, rhenium has a tetrahedral coordination geometry with one methyl and three oxo ligands.
It can be prepared by many routes, a typical method is the reaction of rhenium heptoxide and tetramethyltin:[1] Analogous alkyl and aryl derivatives are known.
Compounds of the type R−ReO3 are Lewis acids, forming both 1:1 and 1:2 adducts with halides and amines.
Methylrhenium trioxide also catalyses the conversion of aldehydes and diazoalkanes into an alkene,[2] and the oxidation of amines to N-oxides with sodium percarbonate.