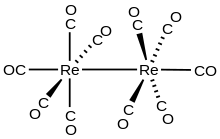
Dirhenium decacarbonyl
[2] The compound consists of a pair of square pyramidal Re(CO)5 units joined via a Re-Re bond, which produces a homoleptic carbonyl complex.
[3] In the 1930s Robert Mond developed methods which used increased pressure and temperature to produce various forms of metal carbonyl .
A prominent scientist of the twentieth century, Walter Hieber was crucial to the further development of specifically the dirhenium decacarbonyl.
[2][6] This compound has a broad IR absorption band at 1800 cm−1 region can be assigned to two components centered at 1780 and 1830 cm−1, resulting from CO adsorption.
[14] Loss of a carbonyl ligand by photolysis generates a coordinatively unsaturated complex that undergoes oxidative addition of Si-H bonds, for example: Rhenium-based catalysis have been used in metathesis, reforming, hydrogenation and various hydrotreating processes such as hydrodesulfurization.