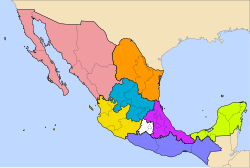
Administrative divisions of Mexico
[1] According to the Constitution of Mexico, the states of the federation are free and sovereign in all matters concerning their internal affairs.
As of March 2024, there are 2,460 municipalities under the 31 states, adding the 16 boroughs of Mexico City to constitute 2476 territorial units with local autonomy.
Two are elected by universal suffrage on the principle of relative majority and one is assigned to the party that obtains the largest minority.
In addition, the federation makes up a constituency in which 32 senators are elected by the method of proportional representation.
Mexico City (Spanish: Ciudad de México) is the capital of the United Mexican States.
However, the Federal District received more autonomy in 1997, and its citizens were then able to elect their chief of government for the first time.
In 2016, the Mexican Congress approved a constitutional reform eliminating the federal district and establishing Mexico City as a fully autonomous entity on par with the states.
[7] *Mexico's post agency, Correos de México, does not offer an official list.
The divisions of municipalities and boroughs are regulated solely by constitutions and laws of the respective federative entities.
Common types of localities include: Some larger cities are consolidated with its own municipality and form a single level governance.
The Treaty of Córdoba recognized part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain as an Independent Empire – "monarchist, constitutional and moderate".
The morning after the Army of the Three Guarantees entered Mexico City on September 28, 1821, Agustín de Iturbide ordered the Supreme Provisional Governmental Junta (September 1821 – February 1822) to meet to elect a president of the Imperial Regency and to issue a declaration of independence for the new nation.
[12] However, the Constitutional Empire quickly demonstrated the incompatibility of its two main parts: the Emperor and the Constituent Congress.
The deputies were imprisoned just for expressing their opinions, and eventually Iturbide decided to dissolve the Congress and instead establish a National Board.
[13] The lack of a legitimate legislature, the illegitimacy of the Emperor, and the absence of real solutions to the nation's problems increased revolutionary activity.
[14] Antonio López de Santa Anna proclaimed the Plan of Casa Mata, to which later joined Vicente Guerrero and Nicolás Bravo.
Iturbide was forced to reestablish the Congress and, in a vain attempt to save the order and keep the situation favorable to his supporters, he abdicated the crown of the empire on March 19, 1823.
The constituent states of the Republic lost their freedom, autonomy, independence, and sovereignty by being totally subordinated to the central government.
The 2nd article posited that the division of the Republic into departments would be under a special law with constitutional character.
This period of political instability caused several conflicts between the central government and the entities of the country, and there were rebellions in several states:[28] On September 11, 1842, the region of Soconusco joined Mexico as part of the department of Chiapas.
The Empire was deposed in 1867 by the republican forces of Benito Juárez and the Federal Republic was restored again under the Constitution of 1857.