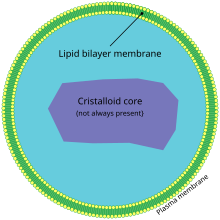
Microbody
A microbody (or cytosome) is a type of organelle that is found in the cells of plants, protozoa, and animals.
[1] Microbodies contain enzymes that participate in the preparatory or intermediate stages of biochemical reactions within the cell.
[2] Two years later in 1956, Rouiller and Bernhard presented the first worldwide accepted images of microbodies in liver cells.
[2] Then in 1965, Christian de Duve and coworkers isolated microbodies from the liver of a rat.
[3] In 1967, Breidenbach and Beevers were the first to isolate microbodies from plants, which they named glyoxysomes because they were found to contain enzymes of the glyoxylate cycle.