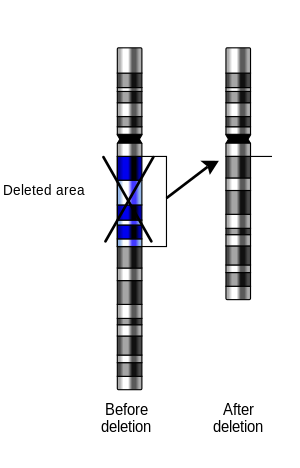
Deletion (genetics)
Deletions that do not occur in multiples of three bases can cause a frameshift by changing the 3-nucleotide protein reading frame of the genetic sequence.
[9] Deletion of part of the short arm of chromosome 5 results in Cri du chat syndrome.
[11] Recent work suggests that some deletions of highly conserved sequences (CONDELs) may be responsible for the evolutionary differences present among closely related species.
[13] The introduction of molecular techniques in conjunction with classical cytogenetic methods has in recent years greatly improved the diagnostic potential for chromosomal abnormalities.
In particular, microarray-comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) based on the use of BAC clones promises a sensitive strategy for the detection of DNA copy-number changes on a genome-wide scale.
[14] Other computation methods were selected to discover DNA sequencing deletion errors such as end-sequence profiling.