Molecular cytogenetics
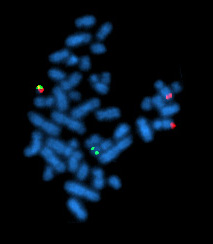
Introduced in the 1980s, FISH uses probes with complementary base sequences to locate the presence or absence of the specific DNA regions.
Virtual karyotypes are generated from arrays made of thousands to millions of probes, and computational tools are used to recreate the genome in silico.
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization maps out single copy or repetitive DNA sequences through localization labeling of specific nucleic acids.
The technique utilizes different DNA probes labeled with fluorescent tags that bind to one or more specific regions of the genome.
[3] It labels all individual chromosomes at every stage of cell division to display structural and numerical abnormalities that may arise throughout the cycle.
FISH maps out single copy or repetitive DNA sequences through localization labeling of specific nucleic acids.
The technique utilizes different DNA probes labeled with fluorescent tags that bind to one or more specific regions of the genome.
For this to work, DNA must be denatured using heat or chemicals to break the hydrogen bonds; this allows hybridization to occur once two samples are mixed.
Virtual karyotypes are generated from microarrays made of thousands to millions of probes, and computational tools are used to recreate the genome in silico.
[6] The labelled DNA samples are co-hybridized to probes during cell division, which is the most informative time for observing copy number variation.
CGH can also scan an entire genome relatively quickly for various chromosome imbalances, and this is helpful in patients with underlying genetic issues and when an official diagnosis is not known.
Using similar principles to CGH, the sample DNA is isolated and fluorescently labelled, then co-hybridized to single stranded probes to generate signals.