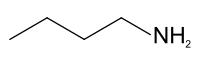
n-Butylamine
This colourless liquid is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being sec-butylamine, tert-butylamine, and isobutylamine.
Its vapours are heavier than air and it produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion.
[3] It is produced by the reaction of ammonia and alcohols over alumina: n-Butylamine is a weak base.
[5] This compound is used as an ingredient in the manufacture of pesticides (such as thiocarbazides), pharmaceuticals, and emulsifiers.
It is also a precursor for the manufacture of N,N′-dibutylthiourea, a rubber vulcanization accelerator, and n-butylbenzenesulfonamide, a plasticizer of nylon.