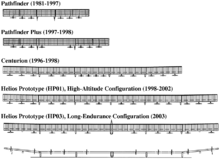
NASA Centurion
The NASA Centurion was the third aircraft developed as part of an evolutionary series of solar- and fuel-cell-system-powered unmanned aerial vehicles.
AeroVironment, Inc. developed the vehicles under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
The ERAST program managers had determined that an aircraft based on the Pathfinder/Pathfinder Plus concept would be the lowest risk approach of achieving the altitude goal.
The full-size Centurion's maiden flight took place at Rogers Dry Lake on November 10, 1998, and lasted a total of 1 hr and 24 minutes.
Although the Centurion shape resembled the Pathfinder, the structure was designed to be stronger and capable of carrying numerous payloads (up to 600 pounds (272.2 kg)) more efficiently.