Nasal surgery
[1] It encompasses several types of techniques, including rhinoplasty, septoplasty, sinus surgery, and turbinoplasty, each with its respective postoperative treatments.
[3] While there are potential risks and complications associated, the advancement of medical instruments and enhanced surgical skills have helped mitigate them.
Nose amputation served as penalisation for war criminals and women deemed indecent, resulting in the demand for nasal reconstruction.
Currently, it comprises four approaches, namely rhinoplasty, septoplasty, sinus surgery, and turbinoplasty, targeted at different sections of the nasal cavity in the order of their external to internal positions.
Surgeons can retrieve smaller tissue grafts from the interior of the nose, while larger ones may be taken from ribs, implants, or other long bones of the patient.
Open rhinoplasty offers a more accessible passage for the surgeon to incise the outer nasal skin, but it may introduce external scarring on the nose.
[11] With respect to the reduced intraoperative loss of tissue and blood, non-surgical rhinoplasty is capable of preventing the occurrence of ischemia or even sepsis.
[12]Septoplasty is a surgical procedure involving the correction of the nasal septum, which refers to the bone and cartilage dividing the space between the nostrils.
When a nasal septum is bent or crooked, it indicates the narrowing or blockage of the airway, leading to breathing difficulties and worsened sinus infections due to poor drainage.
[13] During septoplasty, the surgeon first lifts the mucous membrane enclosing the septum to visualise and assess the cartilage and bone.
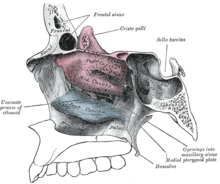
[22] The operation begins with a puncture through the canine fossa, allowing the surgeon to view the bulging of the ethmoid bulla in the maxillary sinus.
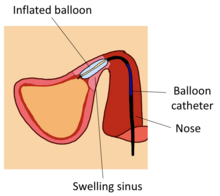
[24] Given the simplicity of the process, around 87% of balloon sinuplasty was conducted as an outpatient procedure, with a duration of approximately thirty minutes and a recovery of one to two days.
To ameliorate intraoperative bleeding, bipolar cautery is used along with the insertion of a Merocell sponge between the turbinate and nasal septum.
Besides preserving the mucosa, shorter operative time, lower blood loss, and improved accuracy are significant advancements brought by microdebrider.
First, an ultrasonic nasal probe is placed along the submucosal lining of the inferior turbinate, and is then moved forward and backward repeatedly.
Compared to radiofrequency turbinoplasty, the destruction of swelling tissues by ultrasound exhibits increased nasal flow and minimal postoperative complications.
Depending on the patient's conditions, doctors may administer medication ranging from nasal steroids that can alleviate mucosal inflammation to antibiotics that can negate the risk of recurrence.
[34][35] After three to five days of ethmoidectomy, the physician will eliminate the middle meatus packing and debride the dried blood clots during a follow-up visit.
[26] Additionally, sinus surgery may potentially result in visual impairment and the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
[18] The loss of vision and haemorrhage can be caused by unintentional injuries of the optic nerve and the internal carotid artery in the ethmoid sinus respectively.
[40] Septoplasty is still considered to be a relatively risky procedure with a high incidence of postoperative complications compared to other types of nasal surgeries.
In response to this, specialists in nasal surgery are working to establish a peer-reviewed classification database that can define each type of anomaly involved.