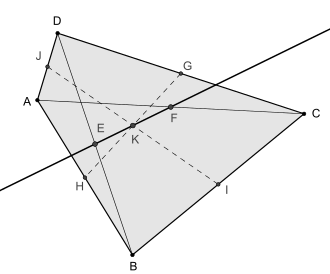
Newton line
In Euclidean geometry the Newton line is the line that connects the midpoints of the two diagonals in a convex quadrilateral with at most two parallel sides.
[1] The line segments GH and IJ that connect the midpoints of opposite sides (the bimedians) of a convex quadrilateral intersect in a point that lies on the Newton line.
This point K bisects the line segment EF that connects the diagonal midpoints.
[1] By Anne's theorem and its converse, any interior point P on the Newton line of a quadrilateral ABCD has the property that where [△ABP] denotes the area of triangle △ABP.
[2] If the quadrilateral is a tangential quadrilateral, then its incenter also lies on this line.