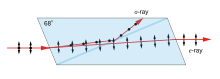
Nicol prism
The Nicol prism consists of a rhombohedral crystal of Iceland spar (a variety of calcite) that has been cut at an angle of 68° with respect to the crystal axis, cut again diagonally, and then rejoined, using a layer of transparent Canada balsam as a glue.
The ordinary ray, or o-ray, experiences a refractive index of no = 1.658 in the calcite and undergoes a total internal reflection at the calcite–glue interface because of its angle of incidence at the glue layer (refractive index n = 1.550) exceeds the critical angle for the interface.
The e-ray merely undergoes a slight refraction, or bending, as it passes through the interface into the lower half of the prism.
The two exiting rays have polarizations orthogonal (at right angles) to each other, but the lower, or e-ray, is the more commonly used for further experimentation because it is again traveling in the original horizontal direction, assuming that the calcite prism angles have been properly cut.
The direction of the upper ray, or o-ray, is quite different from its original direction because it alone suffers total internal reflection at the glue interface, as well as a final refraction on exit from the upper side of the prism.