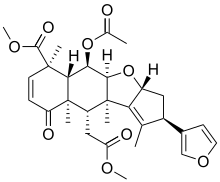
Nimbin (chemical)
Nimbin is thought to be responsible for much of the biological activities of neem oil, and is reported to have anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, fungicidal, antihistamine and antiseptic properties.
Nimbin can be extracted from different parts of the neem tree with a solvent or supercritical carbon dioxide.
[3][4] Nimbin is used for different purposes because it has multiple properties such as insecticide,[5][6] antiviral, antimicrobial,[7] anti-inflammatory,[8] and anti-fungal.
Nimbin is relatively hydrophobic,[14] and there has been a study to make it more hydrophilic with an inclusion complex which can be helpful to enable its direct use.
The final crude is then purified by repeating different silica gel column chromatography with hexane and ethyl acetate (70:30) as a solvent.
In fact, under specific experimental conditions (305 K, 23 MPa and a carbon dioxide flow rate of 0.62 cm3/min) an extraction yield of approximately 85% can be obtained for 2 g of neem.
In this case, methanol can be used as a co-solvent because it's a substantial donor of hydrogen bonds which is responsible for its high solvent power.
Successive intramolecular attack of the H+ on the tertiary carbocation leads to a 180o rotation of bond between C-8 and C-14 and ring closure to produce the rearranged product with cyclic ether: Isonimbin.
To obtain this product, nimbin was taken in a 100mL single-necked round bottom flask fitted with a guard tube, followed by 10mL acetonitrile.
After completion, the flask was immersed in an ice bath, and aqueous ammonia was added slowly until the pH reached 7-8.
The solution was concentrated under reduced pressure using a rotary evaporator, poured into ice-cold water, and extracted using ethyl acetate.
Thus, steric hindrance through the presence of a large group or a lactone ring over the C-28 position may be crucial to transmit cytotoxic activity.
To increase its water solubility, nimbin was put in an inclusion complex with different kinds of cyclodextrins (also called CDs).
There has been an experiment in vitro where NBE could inhibit the pathologic effects of SARS-COV-2 infection on a human lung cell model.
This proves that even though it isn't a direct experiment, we can anticipate that NBE-derived compounds such as nimbin will be able to prevent SARS-COV-2 infection of nasal and lung tissue in vivo as well.
[10][11] Nimbin is one of the best-ranked drugs among the selected natural products showing an inhibitory effect for spike glycoprotein and ACE2 along with curcumin.
Human red blood cell membrane (HBRC) stabilization has been employed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory property.
The reaction of nimbin was tested on hemolysis of human red blood cells induced by heat and hypotonicity.
To detect intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation by induced inflammation (LPS) in zebrafish, an oxidation-sensitive fluorescent DCF-DA sample was used.
As a result, Zebrafish larvae treated with N1, N2, and N3 have been shown to reduce inflammation by decreased in intracellular ROS levels.
The results of the experience confirm that nimbin and its derivatives N1, N2, and N3 have an anti-inflammatory propertie and were able to decrease the ROS levels induced by LPS in both in vivo and in vitro.
A study on zebrafish embryos has made it possible to evaluate the cytotoxic effects of nimbin molecules on the larvae of these fish.
These bacteria present in the soil have the property to induce in many cultivated plants a systemic resistance against various phytopathogenic agents.
A high concentration of neem oil increases the action of nimbin on fungi and thus its antifungal activity.
A study showed that by mixing neem oil with n-hexane or with 90% methanol, nimbin's antifungal activity could be distinguished.
[9] Another study showed that when the oil is mixed with ethanol, neem compounds such as nimbin acted as an inhibitor on fungal colonies.