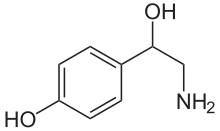
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in the so-called fight-or-flight response.
One of the more notable drugs in the stimulant class is amphetamine, which acts as a dopamine and norepinephrine analog, reuptake inhibitor, as well as an agent that increases the amount of global catecholamine signaling throughout the nervous system by reversing transporters in the synapses.
Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of noradrenaline by blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, are sometimes used to treat glaucoma, migraines and a range of cardiovascular diseases.
β1Rs preferentially bind epinephrine, along with norepinephrine to a lesser extent and mediates some of their cellular effects in cardiac myocytes such as increased positive inotropy and lusitropy.
Alpha blockers, which counter the effects of noradrenaline on alpha-adrenergic receptors, are occasionally used to treat hypertension and psychiatric conditions.
Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating and antihypertensive effect and are commonly used as anesthesia enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence.
The principal end products are either Vanillylmandelic acid or a conjugated form of MHPG, both of which are thought to be biologically inactive and are excreted in the urine.
[17] Once back in the cytosol, norepinephrine can either be broken down by monoamine oxidase or repackaged into vesicles by VMAT, making it available for future release.
[19] This can be contrasted with the acetylcholine-mediated effects of the parasympathetic nervous system, which modifies most of the same organs into a state more conducive to rest, recovery, and digestion of food, and usually less costly in terms of energy expenditure.
It is found that the endocannabinoid anandamide and the cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2 can modify the overall response to sympathetic nerve stimulation, which indicates that prejunctional CB1 receptors mediate the sympatho-inhibitory action.
These noradrenergic cell groups were first mapped in 1964 by Annica Dahlström and Kjell Fuxe, who assigned them labels starting with the letter "A" (for "aminergic").
Noradrenergic cell group A1 is located in the caudal ventrolateral part of the medulla, and plays a role in the control of body fluid metabolism.
[33] It runs at a baseline level during wakefulness, but increases temporarily when a person is presented with any sort of stimulus that draws attention.
Unpleasant stimuli such as pain, difficulty breathing, bladder distension, heat or cold generate larger increases.
It has been argued that this similarity arises because both are to a large degree controlled by the same brain structures, particularly a part of the brainstem called the nucleus gigantocellularis.
[36] Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommended norepinephrine as first line agent in treating septic shock which is unresponsive to fluid resuscitation, supplemented by vasopressin and epinephrine.
They are sometimes used to treat high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, and congestive heart failure, but recent reviews have concluded that other types of drugs are usually superior for those purposes.
[42][43] However, the usefulness of beta blockers is limited by a range of serious side effects, including slowing of heart rate, a drop in blood pressure, asthma, and reactive hypoglycemia.
[44] Some antidepressants function partly as selective alpha-2 blockers, but the best-known drug in that class is yohimbine, which is extracted from the bark of the African yohimbe tree.
[48] Yohimbine acts as a male potency enhancer, but its usefulness for that purpose is limited by serious side-effects including anxiety and insomnia.
[48] Yohimbine is banned in many countries, but in the United States, because it is extracted from a plant rather than chemically synthesized, it is sold over the counter as a nutritional supplement.
[50] Because alpha-2 receptors are inhibitory and many are located presynaptically on norepinephrine-releasing cells, the net effect of these drugs is usually to reduce the amount of norepinephrine released.
[50] Clonidine and guanfacine, for example, are used for the treatment of anxiety disorders and insomnia, and also as a sedative premedication for patients about to undergo surgery.
[52] These are drugs whose primary effects are thought to be mediated by different neurotransmitter systems (dopamine for stimulants, serotonin for antidepressants), but many also increase levels of norepinephrine in the brain.
[citation needed] A number of important medical problems involve dysfunction of the norepinephrine system in the brain or body.
The list of conditions that can cause sympathetic hyperactivation includes severe brain injury,[56] spinal cord damage,[57] heart failure,[58] high blood pressure,[59] kidney disease,[60] and various types of stress.
The consequences can include slowing of growth (in children), sleeplessness, loss of libido, gastrointestinal problems, impaired disease resistance, slower rates of injury healing, depression, and increased vulnerability to addiction.
[64][65] Several conditions, including Parkinson's disease, diabetes, and so-called pure autonomic failure, can cause a loss of norepinephrine-secreting neurons in the sympathetic nervous system.
The symptoms are widespread, the most serious being a reduction in heart rate and an extreme drop in resting blood pressure, making it impossible for severely affected people to stand for more than a few seconds without fainting.
[76] He demonstrated the presence of norepinephrine in sympathetically innervated tissues and brain, and adduced evidence that it is the sympathin of Cannon and Rosenblueth.