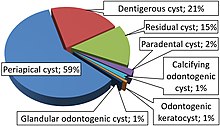
Odontogenic cyst
Intra-bony cysts are most common in the jaws, because the mandible and maxilla are the only bones with epithelial components.
In addition, there are several conditions with so-called (radiographic) 'pseudocystic appearance' in jaws; ranging from anatomic variants such as Stafne static bone cyst, to the aggressive aneurysmal bone cyst.
For example, small radicular cyst may resolved after successful endodontic ("root-canal") treatment.
Because of high recurrence potential and aggressive behaviour, curettage is recommended for keratocyst.
The removed cyst must be evaluated by pathologist to confirm the diagnosis, and to rule out other neoplastic lesions with similar clinical or radiographic features (e.g., cystic or solid ameloblastoma, central mucoepidermoid carcinoma).