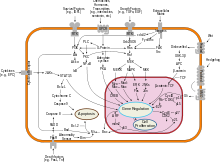
Carcinogenesis
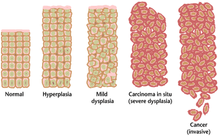
Normally, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, in the form of apoptosis, is maintained to ensure the integrity of tissues and organs.
[13] Genetic and epigenetic changes can occur at many levels, from gain or loss of entire chromosomes, to a mutation affecting a single DNA nucleotide, or to silencing or activating a microRNA that controls expression of 100 to 500 genes.
Genomic amplification occurs when a cell gains many copies (often 20 or more) of a small chromosomal region, usually containing one or more oncogenes and adjacent genetic material.
Among the more than 5,000 compounds in tobacco smoke, the genotoxic DNA-damaging agents that occur both at the highest concentrations, and which have the strongest mutagenic effects are acrolein, formaldehyde, acrylonitrile, 1,3-butadiene, acetaldehyde, ethylene oxide and isoprene.
Other mutations enable the tumor to grow new blood vessels to provide more nutrients, or to metastasize, spreading to other parts of the body.
[40][41] However, it was pointed out by Rubin[42] that "the vast majority of studies in cancer research has been done on well-defined tumors in vivo, or on discrete neoplastic foci in vitro.
[citation needed] If the general process by which sporadic colon cancers arise is the formation of a pre-neoplastic clone that spreads by natural selection, followed by formation of internal sub-clones within the initial clone, and sub-sub-clones inside those, then colon cancers generally should be associated with, and be preceded by, fields of increasing abnormality, reflecting the succession of premalignant events.
The most extensive region of abnormality (the outermost yellow irregular area in the diagram) would reflect the earliest event in formation of a malignant neoplasm.
[44] However, the average number of DNA sequence mutations in the entire genome (including non-protein-coding regions) within a breast cancer tissue sample is about 20,000.
[61] Another concept of cancer development is based on exposure to weak magnetic and electromagnetic fields and their effects on oxidative stress, known as magnetocarcinogenesis.
These early neoplastic changes must be distinguished from hyperplasia, a reversible increase in cell division caused by an external stimulus, such as a hormonal imbalance or chronic irritation.
For example, given that tissue invasion and displacement to distant sites are normal properties of leukocytes, these steps are not needed in the development of leukemia.
For example, inactivation of a single gene, coding for the p53 protein, will cause genomic instability, evasion of apoptosis and increased angiogenesis.
[74][75] Collectively, this reprogramming process induces a stepwise change in cell phenotypes, which will ultimately lead to restoration of tissue function and toward regaining essential structural integrity.
[78] One key factor in healing is the regulation of cytokine gene expression, which enables complementary groups of cells to respond to inflammatory mediators in a manner that gradually produces essential changes in tissue physiology.
[88] NF-κB activates the expression of numerous genes involved in the transition between inflammation and regeneration, which encode cytokines, adhesion factors, and other molecules that can change cell fate.
The activation of aerobic glycolysis (the Warburg effect), which is not necessarily induced by mutations in proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes,[97] provides most of the building blocks required to duplicate the cellular components of a dividing cell and, therefore, is also essential for carcinogenesis.
Mutations in proto-oncogenes, which are the normally quiescent counterparts of oncogenes, can modify their expression and function, increasing the amount or activity of the product protein.
It is important to note that a gene possessing a growth-promoting role may increase the carcinogenic potential of a cell, under the condition that all necessary cellular mechanisms that permit growth are activated.
This makes identification of the stage and type of cancer cell that grows under the control of a given oncogene crucial for the development of treatment strategies.
Often DNA damage will cause the presence of free-floating genetic material as well as other signs, and will trigger enzymes and pathways that lead to the activation of tumor suppressor genes.
The p53 protein, one of the most important studied tumor suppressor genes, is a transcription factor activated by many cellular stressors including hypoxia and ultraviolet radiation damage.
Mutations of tumor suppressor genes that occur in germline cells are passed along to offspring, and increase the likelihood for cancer diagnoses in subsequent generations.
For instance, individuals who inherit one mutant p53 allele (and are therefore heterozygous for mutated p53) can develop melanomas and pancreatic cancer, known as Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
For example, a mutation limited to one oncogene would be suppressed by normal mitosis control and tumor suppressor genes, first hypothesised by the Knudson hypothesis.
Mutation of tumor suppressor genes that are passed on to the next generation of not merely cells, but their offspring, can cause increased likelihoods for cancers to be inherited.
Because mutations in tumor suppressors act in a recessive manner (note, however, there are exceptions), the loss of the normal copy creates the cancer phenotype.
[114] The gastritis caused by H. pylori is accompanied by inflammation, characterized by infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages to the gastric epithelium, which favors the accumulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species/reactive nitrogen species (ROS/RNS).
[119] As reviewed by Santos and Ribeiro[120] H. pylori infection is associated with epigenetically reduced efficiency of the DNA repair machinery, which favors the accumulation of mutations and genomic instability as well as gastric carcinogenesis.
In particular, Raza et al.[121] showed that expression of two DNA repair proteins, ERCC1 and PMS2, was severely reduced once H. pylori infection had progressed to cause dyspepsia.