Oral skills
Oral skills are speech enhancers that are used to produce clear sentences that are intelligible to an audience.
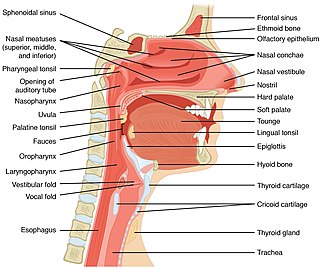
The production speech is insisted by the respiration of air from the lungs that initiates the vibrations in the vocal cords.
The articulation of voice enhances the resonance of speech and enables people to speak intelligibly.
The term "phonation" means the process to produce intelligible sounds for the correct interpretation of speech.
The lungs, vocal cords and larynx play an important role in speech production.
The expanding of the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles builds high pressure in the thoracic cavity.
[1] Vibrations in the vocal cords is achieved by the accelerated movements of the opening and closing of the glottis.
The longer and relaxed the vocal cord are, the slower they vibrate and in turn produces a lower pitch sound.
The vocal folds vibrates in a ‘V’ shape and produces sounds when air passes between the lungs and the glottis.
Oral skills strengthen a speakers ability to produce clear and crisp sounds.
[5] A louder voice can improve the intelligibility of speech when speaking to a larger audience.
[2] The moderate pace in speech enables a listener to process and understand the information.
Speaking at approximately 120-150 words per minute (wpm) is a moderate pace for an audience to comprehend information.
[8] The correct pronunciation of vowels is aided by the soft plate, tongue, lips and cheeks.
The tip of the tongue moves towards the top of the gum ridge to produce words starting with the letter ‘L’.
[8] A verbose tone of voice highlights technical language that is inwardly focused.
Diaphragmatic breathing controls the amount of air the body inhales and exhales and influences the rise and fall of the volume of tone.
that These unintentional pauses can affect the clarity of speech as it creates gaps in the speaker's sentences.
Verbal fillers can disrupt the flow of speech and can distract the attention of the audience.
[10] A pause in a sentence is effective to use than verbal fillers as it does not distract the audience with an unprecedented gap in the information.
Mumbling and not opening the mouth wide enough when speaking can produce unclear speech that is not intelligible.
The human ears detect vibrations from sounds and converts this information to the brain via nerve impulses.
The external, middle and inner ear play an important role in the transformation of sound and energy.
The techniques used in oral skills to produce clear speech impacts the correct interpretation of information.
These vestibule and the semicircular parts play a key role in the sensors for balancing.
Vibrations from the oval window of the inner ear is transferred to the perilymph in the upper canal via a pressure wave.