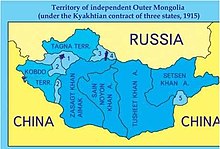
Outer Mongolia
It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia[b] and the Russian republic of Tuva.
The historical region gained de facto independence from Qing China during the Xinhai Revolution.
[4][5][6] Most of Outer Mongolia, however, was under the de facto control of the Bogd Khanate, which was largely unrecognized internationally.
The Republic of China briefly established de facto rule over most of the region from 1919 to 1921.
After the Mongolian People's Republic was founded in 1924, the Nationalist government of China de jure recognized Mongolian independence in 1946 under Soviet pressure,[7] though this recognition was later rescinded by the Kuomintang government in 1953,[c] which had retreated to Taiwan because of continued Soviet support to the Chinese communists.