Paper chemicals
These chemicals can be used to alter the paper in many ways, including changing its color and brightness, or by increasing its strength and resistance to water.
Chemical usage is not only for imparting properties to paper but to handle the water cycles in the process, conditioning of fabrics, cleaning of equipment and several other applications.
There are three predominant methods of bleaching: Most paper types must have some water-resistance to maintain a specific writing quality and printability.
To enhance the paper's strength, cationic starch is added to wet pulp in the manufacturing process.
Dry-strength additives, or dry-strengthening agents, are chemicals that improve paper strength normal conditions.
[7] The surface chemical composition is differentiated by the adsorption of acrylic acid or an anionic surfactant, both of which are used for stabilization of the dispersion in water.
[8] Co-binders, or thickeners, are generally water-soluble polymers that influence the paper's color viscosity, water retention, sizing, and gloss.
Co-binders are used to reduce the cost of the synthetic binder and improve the water retention and rheology of the coating.
[9] China clay, calcium carbonate, titanium dioxide, and talc are common mineral fillers used in paper production.
An additional feature of a retention agent is to accelerate the dewatering in the wire section of the paper machine.
[citation needed] Pigments that absorb in the yellow and red part of the visible spectrum can be added.





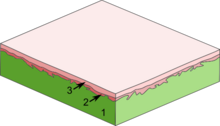
1) The paper or board
2) The first layer of coating to even out the surface
3) A second layer for an even smoother and whiter surface