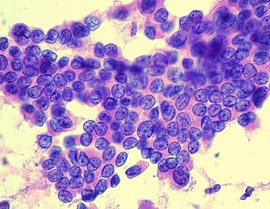
Papillary thyroid cancer
Papillary thyroid carcinomas are also discovered when a hard nodule is found in multinodular goiter, when enlarged cervical lymph nodes are detected, or when there are unidentified metastatic lesions elsewhere in the body.
Other clinical signs that could indicate papillary thyroid are fixation to the trachea, a firm neck mass, damage to recurrent laryngeal or cervical sympathetic nerves.
[9] Reduced expression of ATP5E is significantly associated with the diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer and may serve as an early tumor marker of the disease.
[10] Serum microRNAs have shown good diagnostic performance for distinguishing patients with papillary thyroid cancer from patients with benign thyroid nodules and healthy controls, and are suggested as novel and minimally invasive diagnostic approach in clinical practice.
[20] These kinds of tumors are most commonly unencapsulated, and they have a high tendency to metastasize locally to lymph nodes, which may produce cystic structures near the thyroid that are difficult to diagnose because of the paucity of malignant tissue.
The fusion oncoproteins generated are termed RET/PTC proteins (ret/papillary thyroid carcinoma), and constitutively activate RET and the downstream MAPK/ERK pathway.
[1] Approximately a third to a half of papillary thyroid carcinomas harbor point mutations in the BRAF oncogene, also activating the MAPK/ERK pathway.
After performing a multivariate analysis, it was found that the absence of tumor capsule was the only parameter associated (P=0.0005) with BRAF V600E mutation.
[24] Mitochondrial mutations: MtDNA(mitochondrial) haplogroups, characterized by unique sets of non pathological mtDNA polymorphisms can modulate the pathogenesis of different diseases in specific populations because of its influence on the expression of genes related to ROS production and OXPHOS coupling efficiency and the regulation of apoptosis.
Thyroid lobectomy alone may be sufficient treatment for small (<1 cm), low-risk, unifocal, intrathyroidal papillary carcinomas in the absence of prior head and neck irradiation or radiologically or clinically involved cervical nodal metastasis.
Also, the sternocleidomastoid muscle, jugular vein, and accessory nerve are to be removed if such procedure allows apparently complete tumor resection.
Chemotherapy with cisplatin or doxorubicin has proven limited efficacy, however, it could be helpful for patients with bone metastases to improve their quality of life.
In case of metastases, patients are prescribed antineoplastic agents which inhibit cell growth and proliferation and help in palliating symptoms in progressive disease.
Also, patients may experience a high incidence of nodule metastasis, with 35 percent cases of cervical node metastases.
[32] In light of this data, choosing the optimal course of surgical and medical management of papillary thyroid cancer should involve shared decision making from patient, endocrinologists, and surgeons.
[35] Children with multiple lung metastases and/or a miliary aspect still have an excellent long-term prognosis if given adequate treatment.