Adrenal cortex
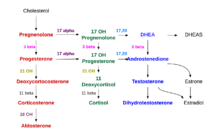
[2] The adrenal cortex comprises three main zones, or layers that are regulated by distinct hormones as noted below.
[6] Aldosterone's effects are on the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct of the kidney where it causes increased reabsorption of sodium and increased excretion of both potassium (by principal cells) and hydrogen ions (by intercalated cells of the collecting duct).
[6] Sodium retention is also a response of the distal colon, and sweat glands to aldosterone receptor stimulation.
[10] Situated between the glomerulosa and reticularis, the cells of the zona fasciculata synthesize and secrete glucocorticoids (such as 11-deoxycorticosterone, corticosterone, and cortisol), as well as small amounts of adrenal androgens and estrogens.
[9] The major hormone that stimulates cortisol secretion in humans is the ACTH that is released from the anterior pituitary.
[8] The innermost cortical layer, the zona reticularis, produces adrenal androgens, as well as small amounts of estrogens and some glucocorticoids.
[6] Aldosterone effects on the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct of the kidney where it causes increased reabsorption of sodium and increased excretion of both potassium (by principal cells) and hydrogen ions (by intercalated cells of the collecting duct).
[6] Sodium retention is also a response of the distal colon, and sweat glands to aldosterone receptor stimulation.