Parallel processing (DSP implementation)
In digital signal processing (DSP), parallel processing is a technique duplicating function units to operate different tasks (signals) simultaneously.
[1] Accordingly, we can perform the same processing for different signals on the corresponding duplicated function units.
The required time for the function unit
Then, if we operate these three tasks in a sequential order, the required time to complete them is
However, if we duplicate the function unit to another two copies (
Mechanism: Objective: Consider a condition that we are able to apply both parallel processing and pipelining techniques, it is better to choose parallel processing techniques with the following reasons Consider a 3-tap FIR filter:[2] which is shown in the following figure.
The sample period is given by By parallelizing it, the resultant architecture is shown as follows.
The sample rate now becomes where N represents the number of copies.
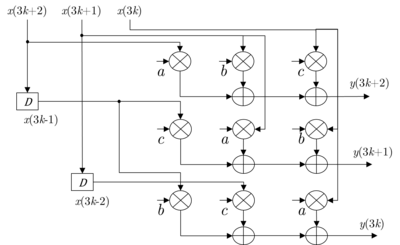
Consider the transfer function of a 1st-order IIR filter formulated as where |a| ≤ 1 for stability, and such filter has only one pole located at z = a; The corresponding recursive representation is Consider the design of a 4-parallel architecture (N = 4).
In such parallel system, each delay element means a block delay and the clock period is four times the sample period.
The resultant parallel design has the following properties.
The square increase in hardware complexity can be reduced by exploiting the concurrency and the incremental computation to avoid repeated computing.
Another advantage for the parallel processing techniques is that it can reduce the power consumption of a system by reducing the supply voltage.
Consider the following power consumption in a normal CMOS circuit.
where the Ctotal represents the total capacitance of the CMOS circuit.
In order to maintain the same sample rate, the clock period of the N-parallel circuit increases to N times the propagation delay of the original circuit.
Therefore, the power consumption of the N-parallel system can be formulated as where β can be computed by