Parliamentary republic
In some countries the head of state has reserve powers to use at their discretion as a non-partisan "referee" of the political process.
The Fourth Republic saw an era of great economic growth in France and the rebuilding of the nation's social institutions and industry after the war, and played an important part in the development of the process of European integration, which changed the continent permanently.
As a result, the Fourth Republic collapsed and Charles de Gaulle was given power to rule by decree, subsequently legitimized by approval of a new constitution in a referendum on 28 September 1958 that led to the establishment of the French Fifth Republic in 1959.
In the case of many republics in the Commonwealth of Nations, it was common for the Sovereign, formerly represented by a Governor-General, to be replaced by a non-executive head of state.
This was the case in South Africa (which ceased to be a member of the Commonwealth immediately upon becoming a republic, and later switched to having an executive presidency), Malta, Trinidad and Tobago, India, Vanuatu and since 30 November 2021, Barbados.
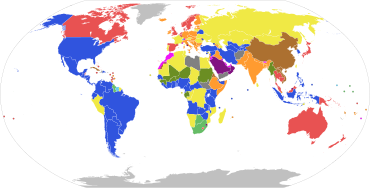
Parliamentary systems : Head of government is elected or nominated by and accountable to the legislature
Presidential system : Head of government (president) is popularly elected and independent of the legislature
Hybrid systems:
Other systems:
Note: this chart represents the de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.