Peaking power plant
[8] Australia's Clean Energy Council found in April 2021 that battery storage can be 30% cheaper than gas peaker plants.
In hot climates, the peak is usually late afternoon when air conditioning load is high, during this time many workplaces are still open and consuming power.
In addition to natural gas, many peaker plants are able to use petroleum as a backup fuel, storing oil in tanks on site.
This option, in combination with a thermal energy storage tank, can increase the turbine power output in on-peak periods up to 30%.
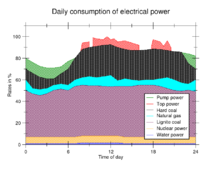
Natural gas turbines or pumped storage are often used where there is not enough hydroelectricity to respond to daily and weekly variations in generation and consumption.
[14] The ability to vary the amount of electricity generated is often limited by the requirement that minimum or maximum flows downstream are satisfied.
[15] Pumped-storage hydroelectricity is the largest-capacity form of grid energy storage available, used for averaging off-peak and peak electrical demands.
Pumped-storage and batteries are net consumers, as they have no inherent energy source, and the conversion between electricity and storage and back incurs some losses.
These generating units will emphasize low incremental fuel cost, but may use a higher capital investment to improve efficiency.
Since a steam cycle power plant may take hours to go from cold standby to full rating, they are not usually used to provide peak load service.
[24] Intermediate load following power plants such as hydroelectric operate between these extremes, curtailing their output on nights and weekends when demand is low.