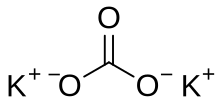
Potassium carbonate
It is a white salt, which is soluble in water and forms a strongly alkaline solution.
Potassium carbonate is the primary component of potash and the more refined pearl ash or salt of tartar.
Historically, pearl ash was created by baking potash in a kiln to remove impurities.
[5] In late 18th-century North America, before the development of baking powder, pearl ash was used as a leavening agent for quick breads.
[6][7] The modern commercial production of potassium carbonate is by reaction of potassium hydroxide with carbon dioxide:[3] From the solution crystallizes the sesquihydrate K2CO3·1.5H2O ("potash hydrate").