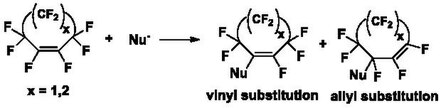
Perfluorocycloalkene
PFCAs have shown reactivity with a wide variety of nucleophiles including phenoxides, alkoxides, organometallic, amines, thiols, and azoles.
[1] They or their derivatives are reported to have nonlinear optical activity,[2] and be useful as lubricants,[3] etching agents,[4] components of fuel cells,[5] low-dielectric materials, and superhydrophobic and oleophobic coatings.
[6] Derivatization of these PFCA rings via displacement of fluorine atoms with nucleophiles occurs through an addition-elimination reaction in the presence of a base.
The ratio of vinylic to allylic products depends on the ring size, reaction conditions, and nucleophile.
A unique class of aromatic ether polymers containing perfluorocyclopentenyl (PFCP) enchainment was prepared from the simple step-growth polycondensation of commercial available bisphenols and octafluorocyclopentene (OFCP) in the presence of triethylamine (Scheme 3 and 4).