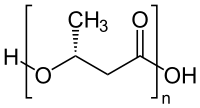
Condensation polymer
Natural proteins as well as some common plastics such as nylon and PETE are formed in this way.
Linear polymers are produced from bifunctional monomers, i.e. compounds with two reactive end-groups.
Common condensation polymers include polyesters, polyamides such as nylon, polyacetals, and proteins.
When prepared from amino-carboxylic acids, e.g. amino acids, the stoichiometry of the polymerization includes co-formation of water: When prepared from diamines and dicarboxylic acids, e.g. the production of nylon 66, the polymerization produces two molecules of water per repeat unit: Another important class of condensation polymers are polyesters.
The peptide or ester bonds between monomers can be hydrolysed, especially in the presence of catalysts or bacterial enzymes.