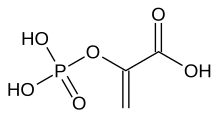
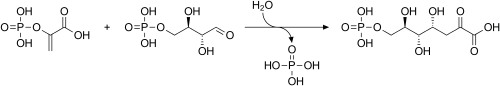Phosphoenolpyruvic acid
Phosphoenolpyruvate (2-phosphoenolpyruvate, PEP) is the carboxylic acid derived from the enol of pyruvate and phosphate.
In plants, it is also involved in the biosynthesis of various aromatic compounds, and in carbon fixation; in bacteria, it is also used as the source of energy for the phosphotransferase system.
PEP is formed from the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate and hydrolysis of one guanosine triphosphate molecule.
This reaction is a rate-limiting step in gluconeogenesis:[3] Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.
In addition, in C4 plants, PEP serves as an important substrate in carbon fixation.