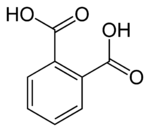
Phthalic acid
[4] Phthalic acid was first obtained by French chemist Auguste Laurent in 1836 by oxidizing naphthalene tetrachloride.
[5][6][7] After the Swiss chemist Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac determined its correct formula,[8] Laurent gave it its present name.
[5][9][10] Manufacturing methods in the nineteenth century included oxidation of naphthalene tetrachloride with nitric acid, or, better, oxidation of the hydrocarbon with fuming sulfuric acid, using mercury or mercury(II) sulfate as a catalyst.
The monopotassium salt, potassium hydrogen phthalate is a standard acid in analytical chemistry.
Reduction of phthalic acid with sodium amalgam in the presence of water gives the 1,3-cyclohexadiene derivative.