Polymethine dyes
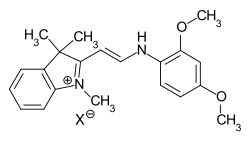
general structure of hemicyanine dyesIf both terminal amino and imino groups of the chromophore are open chain, one speaks of streptocyanine dyes.
[6] general structure of merocyanine dyesMembers of the oxonol dyes, whose terminal groups contain oxygen as heteroatom, play a role in analogue colour photography[8] and the following of enzymatic reactions via the use of barbituric and thiobarbituric terminal groups.
[9][10] general structure of oxonol dyesBy condensing an active methylene compound (e.g. malonic acid dinitrile) with a benzaldehyde derivative, styryl dyes are obtained.
By integrating a benzene ring into the polyene part, these compounds have a styrene partial structure.
Disperse Yellow 31 (3)Also amino- and hydroxy-substituted di- and triarylmethines comprise the structural element of a methine dye: Triarylmethine dyes, resonance structure (R=H, alkyl)Triarylmethine dyes are derived from triphenylmethane, in which at least two of the aromatic rings have electron-donating substituents (e.g. amino groups, secondary and tertiary alkylamino groups or hydroxy groups).
58 Triarylmethine dyes usually show intensive, luminous colourings with different light fastness.