Precipitation types
Orographic precipitation occurs when moist air is forced upwards over rising terrain and condenses on the slope, such as a mountain.
Stratiform precipitation occurs when large air masses rise diagonally as larger-scale winds and atmospheric dynamics force them to move over each other.
Convection occurs when the Earth's surface, especially within a conditionally unstable or moist atmosphere, becomes heated more than its surroundings and in turn leading to significant evapotranspiration.
In the initial stages of this precipitation, it generally falls as showers with a smaller area and a rapidly changing intensity.
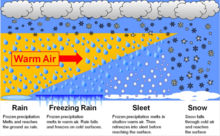
The warmer air is forced to rise and, if conditions are right, creates an effect of saturation and condensation, causing precipitation.
Precipitation duration is often shorter and generally more intense than that which occurs ahead of warm fronts.
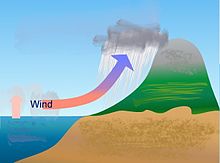
Orographic or relief rainfall is caused when masses of air are forced up the side of elevated land formations, such as large mountains or plateaus (often referred to as an upslope effect).
The lift of the air up the side of the mountain results in adiabatic cooling with altitude, and ultimately condensation and precipitation.
Moisture is precipitated and removed by orographic lift, leaving drier air (see Foehn) on the descending (generally warming), leeward side where a rain shadow is observed.
Local climates vary considerably on each island due to their topography, divisible into windward (Koʻolau) and leeward (Kona) regions based upon location relative to the higher surrounding mountains.
In South America, the Andes mountain range blocks Pacific Ocean winds and moisture that arrives on the continent, resulting in a desert-like climate just downwind across western Argentina.
Precipitation is measured using a rain gauge, and more recently remote sensing techniques such as a weather radar.