Predation
Spiders are predatory, as well as other terrestrial invertebrates such as scorpions; centipedes; some mites, snails and slugs; nematodes; and planarian worms.
[12] Methods of predation by plants varies greatly but often involves a food trap, mechanical stimulation, and electrical impulses to eventually catch and consume its prey.
[21] Many species of protozoa (eukaryotes) and bacteria (prokaryotes) prey on other microorganisms; the feeding mode is evidently ancient, and evolved many times in both groups.
In between, plovers and other shorebirds, freshwater fish including crappies, and the larvae of coccinellid beetles (ladybirds), alternate between actively searching and scanning the environment.
It is a good fit to the behaviour of a wide variety of organisms including bacteria, honeybees, sharks and human hunter-gatherers.
[25][39][12] Another strategy in between ambush and pursuit is ballistic interception, where a predator observes and predicts a prey's motion and then launches its attack accordingly.
[41][40] Vertebrate ambush predators include frogs, fish such as the angel shark, the northern pike and the eastern frogfish.
[49] An extreme form of pursuit is endurance or persistence hunting, in which the predator tires out the prey by following it over a long distance, sometimes for hours at a time.
The African wild dog is an extreme persistence predator, tiring out individual prey by following them for many miles at relatively low speed.
[57] By hunting socially chimpanzees can catch colobus monkeys that would readily escape an individual hunter, while cooperating Harris hawks can trap rabbits.
[22][71] Under the pressure of natural selection, predators have evolved a variety of physical adaptations for detecting, catching, killing, and digesting prey.
These include speed, agility, stealth, sharp senses, claws, teeth, filters, and suitable digestive systems.
[88][89] The marbled sea snake that has adapted to egg predation has atrophied venom glands, and the gene for its three finger toxin contains a mutation (the deletion of two nucleotides) that inactives it.
[117][118] Many pursuit predators that run on land, such as wolves, have evolved long limbs in response to the increased speed of their prey.
[125] A more symmetric arms race may occur when the prey are dangerous, having spines, quills, toxins or venom that can harm the predator.
In western North America, the common garter snake has developed a resistance to the toxin in the skin of the rough-skinned newt.
As energy moves up the trophic levels, it decreases due to heat, waste, and the natural metabolic processes that occur as predators consume their prey.
Increased browsing on willows and conifers along Blacktail Creek due to a lack of predation caused channel incision because the reduced beaver population was no longer able to slow the water down and keep the soil in place.
[143] However, attempts to reproduce the predictions of this model in the laboratory have often failed; for example, when the protozoan Didinium nasutum is added to a culture containing its prey, Paramecium caudatum, the latter is often driven to extinction.
If this rate is limited by time spent handling each catch, then prey populations can reach densities above which predators cannot control them.
In reality, predators tend to select young, weak, and ill individuals, leaving prey populations able to regrow.
[149] As a result, population cycles tend to be found in northern temperate and subarctic ecosystems because the food webs are simpler.
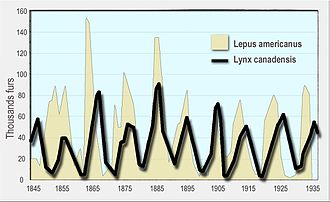
[150] The snowshoe hare-lynx system is subarctic, but even this involves other predators, including coyotes, goshawks and great horned owls, and the cycle is reinforced by variations in the food available to the hares.
[5] Predation visibly became important shortly before the Cambrian period—around 550 million years ago—as evidenced by the almost simultaneous development of calcification in animals and algae,[161] and predation-avoiding burrowing.
[164] Auroralumina attenboroughii is an Ediacaran crown-group cnidarian (557–562 mya, some 20 million years before the Cambrian explosion) from Charnwood Forest, England.
[166] Among the Cambrian predators were invertebrates like the anomalocaridids with appendages suitable for grabbing prey, large compound eyes and jaws made of a hard material like that in the exoskeleton of an insect.
[167] Some of the first fish to have jaws were the armoured and mainly predatory placoderms of the Silurian to Devonian periods, one of which, the 6 m (20 ft) Dunkleosteus, is considered the world's first vertebrate "superpredator", preying upon other predators.
[168][169] Insects developed the ability to fly in the Early Carboniferous or Late Devonian, enabling them among other things to escape from predators.
Natural predators, provided they do no harm to non-pest species, are an environmentally friendly and sustainable way of reducing damage to crops and an alternative to the use of chemical agents such as pesticides.
[186] Attitudes to large predators in North America, such as wolf, grizzly bear and cougar, have shifted from hostility or ambivalence, accompanied by active persecution, towards positive and protective in the second half of the 20th century.