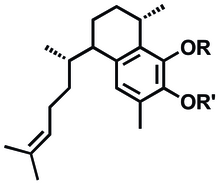
Pseudopterosin A
Pseudopterosin A is a diterpene glycoside isolated from the gorgonian sea whip Antillogorgia elisabethae, found in the Bahamas and Florida Keys.
[1] Pseudopterosins A-D, which differ in the degree of acetylation at the sugar ring, were first isolated and reported in 1986.
[1] Samples of P. elisabethae from the Bahamas are found to have higher concentrations of pseudopterosins than populations from the Florida Keys, which have a greater diversity in diterpene structures.
[4] Commercially, pseudopterosins are found in skin creams as topical anti-inflammatory agents.
The proposed synthesis of artificial anti-inflammatory metabolites is modeled after pseudopterosins and is based on the bicyclic seco-pseudopterosin structure 6.