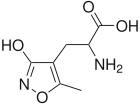
Analeptic
Analeptics can also be used as convulsants, with low doses causing patients to experience heightened awareness, restlessness, and rapid breathing.
[3] Analeptics have been used throughout history for two main purposes, to help patients recover from anesthesia more efficiently and to manage respiratory distress and apnea, particularly in infants.
In clinical settings, analeptics such as doxapram have been used to help patients recover from anesthesia better, as well as to remove some of the potential negative side effects of potent anesthetics.
The three most prevalent clinical analeptic uses of caffeine are in the treatment of asthma, apnea of prematurity, and bronchopulmonary dysplasia in newborn infants.
[6] This cessation of breathing is due to the underdevelopment of the body's respiratory control center, the medulla oblongata, in premature infants.
Ample research also suggests that caffeine significantly reduces the occurrence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia, which is a chronic lung disorder defined by the need for supplemental oxygen after a postmenstrual age of 36 weeks.
Analeptics can act as potassium channel blockers, ampakines, serotonin receptor agonists, and adenosine antagonists.
These cells are responsible for sensing low concentrations of oxygen and transmitting information to the CNS, ultimately leading to an increase in respiration.
Ligand binding causes AMPA receptors to open and allow for sodium ions to flow into the cell, leading to depolarization and signal transduction.
Increased adenosine levels are known to cause depression of spontaneous electrical activity of the neurons, inhibition of neurotransmission, and decreased release of neurotransmitters.
The side effects of doxapram are rare, but with overdose, hypertension, tachycardia, tremors, spasticity, and hyperactive reflexes have been seen to occur.
[10] Between 1930 and 1960, synthetic analeptics such as nikethamide, pentylenetetrazol, bemegride, amphetamine, and methylphenidate replaced the naturally occurring compounds in treating barbiturate overdose.
Recently, analeptics have been turned to the treatment of ADHD due to more efficient ways to treat barbiturate overdoses.